Interact with the Front-end
Creating a user-friendly web interface for smart contracts on the Rootstock network enhances user interaction. Here, we'll focus on using Wagmi and RainbowKit, some popular libraries for connecting your smart contracts to a web front-end.
Project Setup
-
Create a new web project. In this case, we'll be using Next.js as our web framework.
npx create-next-app@latest -
Go to the root of your Next.js project and, using your preferred package manager, install these dependencies:
yarn add @rainbow-me/rainbowkit wagmi viem@2.x @tanstack/react-query -
Create an
.envfile at the root of your project and add the following content. You can get your Wallet Connet ID from WalletConnect Dashboard.touch .env.local
echo "NEXT_PUBLIC_WC_PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>" >> .env.local -
Create a
providers.tsxfile inside theappdirectory and add the following content:"use client";
import {
getDefaultConfig,
RainbowKitProvider,
} from "@rainbow-me/rainbowkit";
import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider } from "@tanstack/react-query";
import { WagmiProvider } from "wagmi";
import { rootstock, rootstockTestnet } from "wagmi/chains";
const config = getDefaultConfig({
appName: "Rootstock Wagmi Starter",
projectId: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_WC_PROJECT_ID as string,
chains: [rootstockTestnet, rootstock],
ssr: true,
});
const queryClient = new QueryClient();
export default function Providers({
children,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode;
}) {
return (
<WagmiProvider config={config}>
<QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}>
<RainbowKitProvider>{children}</RainbowKitProvider>
</QueryClientProvider>
</WagmiProvider>
);
} -
And now import and use the
Providerscomponent to wrap your application in thelayout.tsxfile inside theappdirectory:import type { Metadata } from "next";
import "./globals.css";
import localFont from "next/font/local";
import Providers from "./providers";
import "@rainbow-me/rainbowkit/styles.css";
export const metadata: Metadata = {
title: "Rootstock Wagmi Starter",
description:
"Interact with contracts on Rootstock Network with Wagmi and RainbowKit",
};
const geistSans = localFont({
src: "./fonts/GeistVF.woff",
variable: "--font-geist-sans",
weight: "100 900",
});
const geistMono = localFont({
src: "./fonts/GeistMonoVF.woff",
variable: "--font-geist-mono",
weight: "100 900",
});
export default function RootLayout({
children,
}: Readonly<{
children: React.ReactNode;
}>) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body
className={`${geistSans.variable} ${geistMono.variable} antialiased`}
>
<Providers>{children}</Providers>
</body>
</html>
);
} -
Finally, start the web server.
yarn dev
If everything went well, you should be able to access your web app by navigating to http://localhost:3000 in your browser.
Congrats!
You're all set up. Let's get to the smart contract interaction.
Call Smart Contract using Connect Button and Wagmi hooks
We're going to be editing the page.tsx file inside the app directory. Follow these steps to interact with the smart contract:
-
Delete the default content and add the
<ConnectButton />component to check if it's working fine.import { ConnectButton } from "@rainbow-me/rainbowkit";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className="flex flex-col justify-center items-center min-h-screen">
<ConnectButton /> <!-- RainbowKit Connect Button component -->
</main>
);
}And you should see something like this in the browser:
Please try connecting your wallet.
-
Now we're going to use our first hook from Wagmi to check if a user wallet is connected and, if so, get the connected address. The hook is
useAccountand is used like this:const {
address, // Connected address
isConnected, // true if a wallet is connected
} = useAccount();Note: As we're using react hooks in a Next.js project, don't forget to add the
'use client'directive at the top of yourpage.tsxfile.Now that we know if a wallet is connected, we can add some conditional rendering content and show the connected address.
{
isConnected && <p>Connected address: {address}</p>;
}So the full code on the
page.tsxfile should be something like this:"use client";
import { ConnectButton } from "@rainbow-me/rainbowkit";
import { useAccount } from "wagmi";
export default function Home() {
const { isConnected, address } = useAccount();
return (
<main className="flex flex-col justify-center items-center min-h-screen gap-3">
<ConnectButton />
{isConnected && <p>Connected address: {address}</p>}
</main>
);
}And the browser should look something like this:

-
We're now going to make our first read from the blockchain. The hook we're using for that is
useReadContractand is used like this:const {
data: balance, // Retrieved data from the function
isLoading, // Check if the data is still being fetched
error, // Check if an error occurred
} = useReadContract({
address: "<YOUR_CONTRACT_ADDRESS>", // Your deployed contract address
abi: [
// Contract abi
],
functionName: "balanceOf", // The name of the function you want to call
args: [address], // Function arguments if they are required
});Given this, we need to bring the contract abi that should be available at the Hardhat project we've been working on. Once you compile a contract, a file is generated at
artifacts/contracts/YourContract.sol/YourContract.jsonwhich contains the abi of the contract.In this case, we're going to copy the abi array and paste it in a new file called
MyContractAbi.tsinside a newassetsfolder. the file should look like this:// assets/MyContractAbi.ts
export const abi = [
{
inputs: [
{
internalType: "uint256",
name: "initialSupply",
type: "uint256",
},
],
stateMutability: "nonpayable",
type: "constructor",
},
...
];Now, lets compose our
useReadContracthook with our contract information and show the balance of the connected address:"use client";
import { abi } from "@/assets/MyTokenAbi";
import { ConnectButton } from "@rainbow-me/rainbowkit";
import { useAccount, useReadContract } from "wagmi";
const CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0x543ba9fc0ade6f222bd8c7bf50a0cd9923faf569"; // Replace with your contract address
export default function Home() {
const { isConnected, address } = useAccount();
const {
data: balance,
isLoading,
error,
} = useReadContract({
// Once the component is mounted, useReadContract is called
address: CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
functionName: "balanceOf",
args: [address], // Replace with the address you want to check
});
return (
<main className="flex flex-col justify-center items-center min-h-screen gap-3">
<ConnectButton />
{isConnected && (
<>
<p>Connected address: {address}</p>
<p>
<span className="font-bold">Balance:</span>{" "}
{
isLoading // Check if the data is still being fetched
? "Loading..."
: error // Check if there was an error
? "Error retrieving balance"
: balance?.toString() // If the data is ready, display the balance
}
</p>
</>
)}
</main>
);
}And the browser should look something like this:
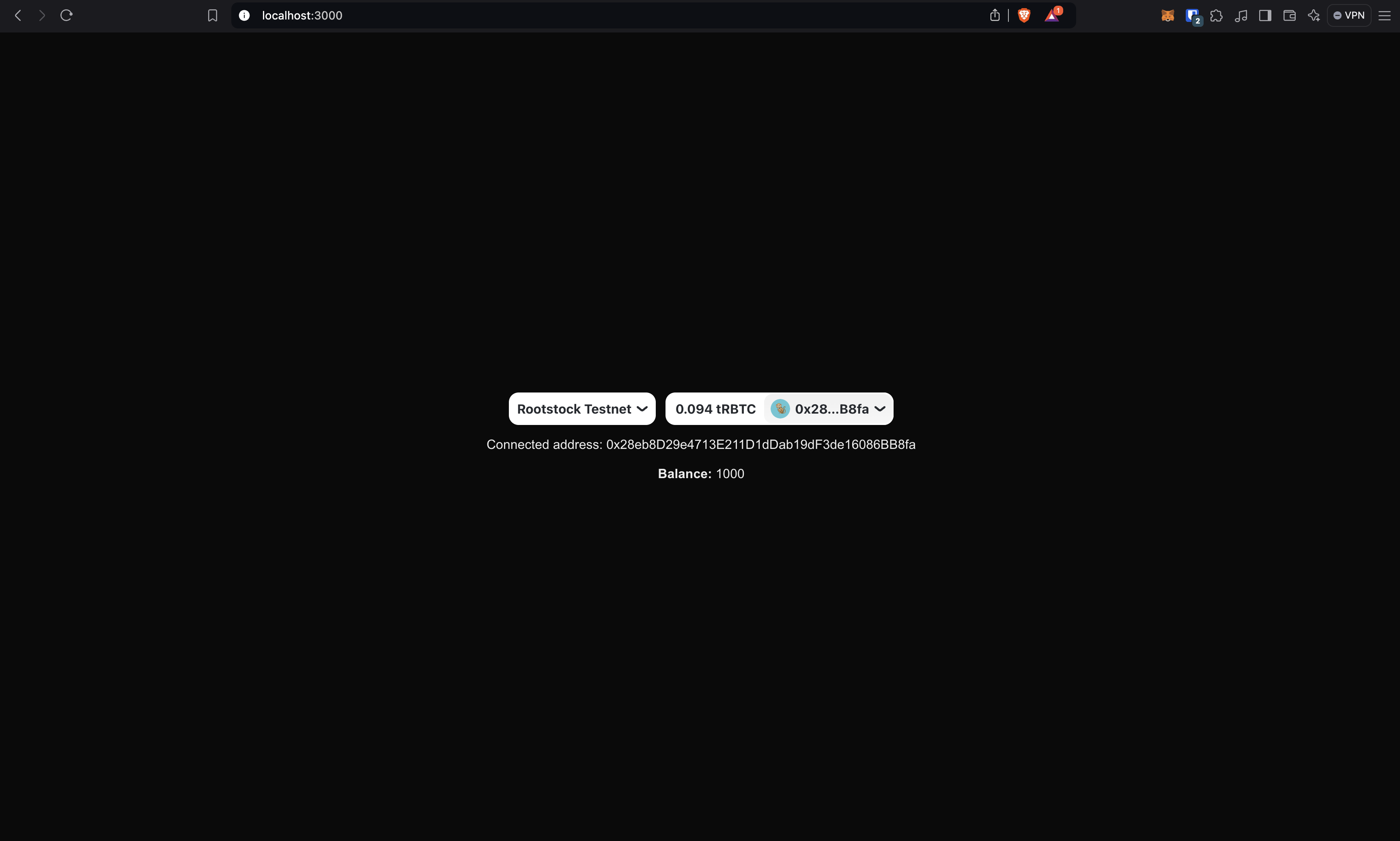
Well done!
You made your first read from the Rootstock blockchain in a web application. Now let's move on to the writing.
-
The hook we're using for calling a write function is
useWriteContract. When calling write functions, I recommend mixing the hook with another wagmi tool calledwaitForTransactionReceipt. Later in the article we'll see why it is important and how to use it. For now, this is how you useuseWriteContracthook.const {
writeContractAsync, // The callable asynchronous function
} = useWriteContract();And the
writeContractAsyncfunction is called very similar to theuseReadContracthook:const hash = await writeContractAsync({
address: CONTRACT_ADDRESS, // Your deployed contract address
abi, // Contract abi
functionName: "mint", // The name of the function you want to call
args: [address, amount], // Function arguments if they are required
});The
writeContractAsyncfunction returns a hash that enables thewaitForTransactionReceiptpower. ThewaitForTransactionReceiptfunction allows you to wait until the transaction is confirmed the number of times you specify. You can call it like this:await waitForTransactionReceipt(
config, // the wagmi config
{
hash, // the transaction hash
confirmations: 1, // the number of confirmations to wait for
}
);Note: Sometimes getting the wagmi config can be a bit tricky. You can get it very easily using the
useConfighook. In the next section we'll see how to do it.So, now that we have all things needed, we're creating a button that will allow us to transfer tokens. For now, we'll fix the token amount to 10 and the address, but you can modify this starter kit as you can, your imagination is the limit. Your code should look something like this:
"use client";
import { abi } from "@/assets/MyTokenAbi";
import { ConnectButton } from "@rainbow-me/rainbowkit";
import { useState } from "react";
import {
useAccount,
useConfig,
useReadContract,
useWriteContract,
} from "wagmi";
import { waitForTransactionReceipt } from "wagmi/actions";
const CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0x543ba9fc0ade6f222bd8c7bf50a0cd9923faf569";
export default function Home() {
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false); // Add loading state
const config = useConfig(); // Get the wagmi config
const { isConnected, address } = useAccount();
const {
data: balance,
isLoading,
error,
refetch,
} = useReadContract({
address: CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
functionName: "balanceOf",
args: [address],
});
const { writeContractAsync } = useWriteContract(); // get the callable write contract function
async function handleTransfer() {
try {
setLoading(true);
const hash = await writeContractAsync({
address: CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
functionName: "transfer",
args: ["0x4913AbCD40a9455a28134b4ccc37f4f95225e593", 10], // Replace with the address and amount you want to transfer
});
await waitForTransactionReceipt(config, {
hash,
confirmations: 1,
});
refetch(); // Refetch the balance after transfer
} catch (error) {
alert("Error transferring MTK. Look at the console.");
console.error(error);
} finally {
setLoading(false);
}
}
return (
<main className="flex flex-col justify-center items-center min-h-screen gap-3">
<ConnectButton />
{isConnected && (
<>
<p>Connected address: {address}</p>
<p>
<span className="font-bold">Balance:</span>{" "}
{isLoading
? "Loading..."
: error
? "Error retrieving balance"
: balance?.toString()}
</p>
<button
className="bg-blue-500 hover:bg-blue-700 disabled:pointer-events-none disabled:opacity-60 text-white font-bold py-2 px-4 rounded"
disabled={loading} // Disable the button if transaction is in progress
onClick={handleTransfer}
>
{loading
? "Transferring..." /* Display "Transferring..." if transaction is in progress */
: "Transfer MTK"}
</button>
</>
)}
</main>
);
}Note: Please make sure you have available tokens in your wallet before transferring. Otherwise, you'll get an error.
Note that we retrieved the
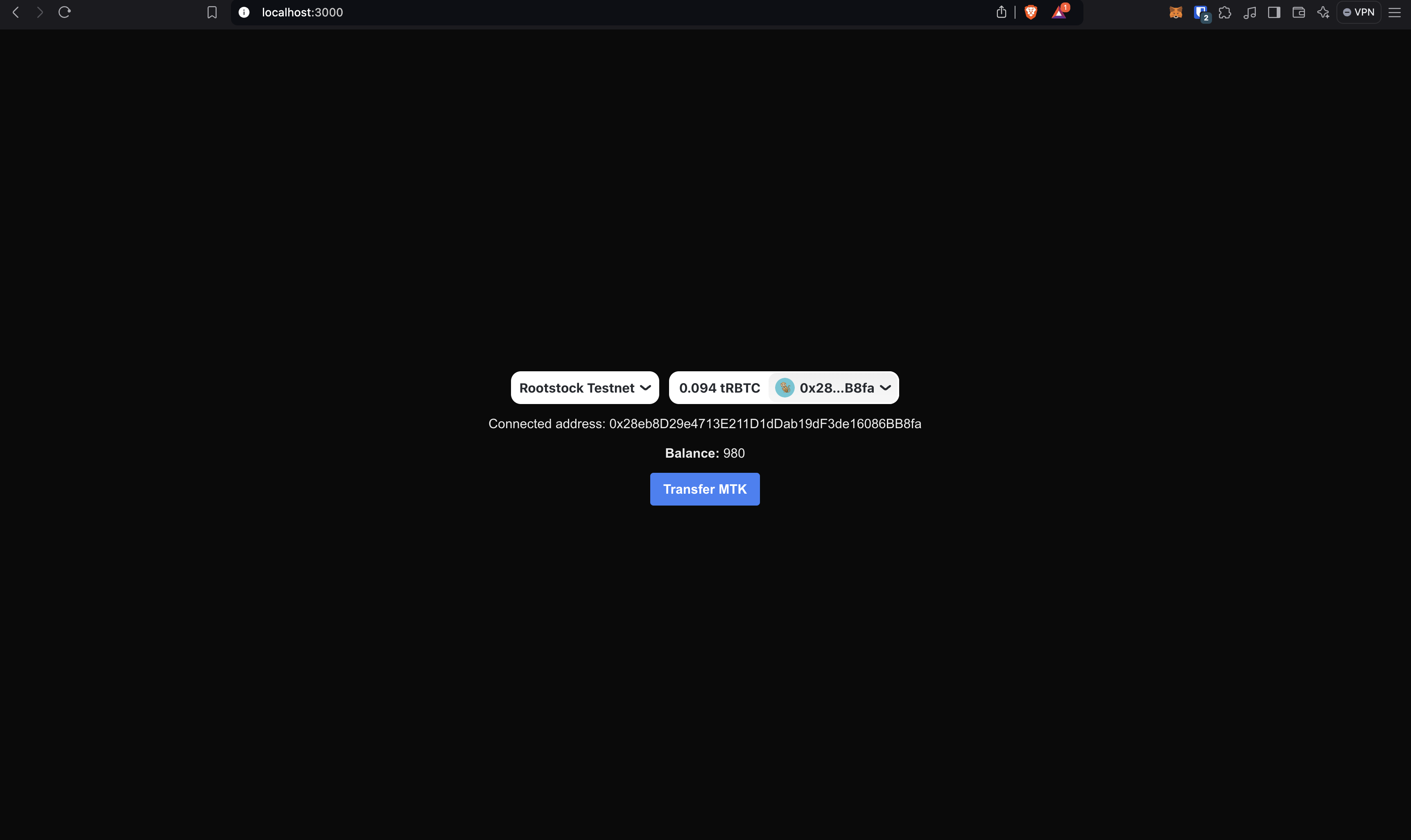
refetchfunction from theuseReadContracthook. This allows us to refetch the balance after the transfer. Also, there is shown how to use theuseConfighook to get the wagmi config.By now, the page should look something like this:
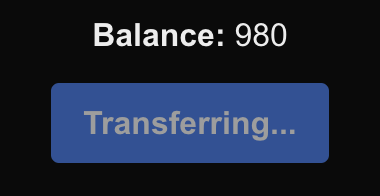
When transferring, the button should look something like this:
And when the transfer is complete, the balace should update immediately:
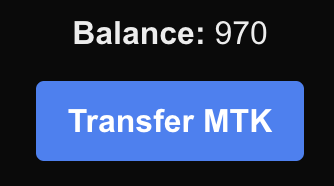
Well done!
You just made created a dApp that allows you to send write/read transactions to the Rootstock blockchain!
Resources
These tools are specifically designed to make Web3 development smoother, particularly for integrating blockchain functionalities into web applications. Below is a list of key libraries and tools that were used in the article, with brief explanations:
- RainbowKit is a React library offering a comprehensive wallet connection solution. It provides a beautiful, easy-to-use wallet connection interface that supports multiple wallets and networks.
- Why Use It: It is great for projects where you want a seamless and user-friendly wallet connection experience. It's easy to integrate and manage, especially in React-based applications.
- Wagmi is a set of React Hooks for Ethereum that simplifies interactions with ethers.js. It provides hooks for wallet connection, contract interaction, balances, and more.
- Why Use It: For React developers who prefer a hooks-based approach, Wagmi offers an elegant way to integrate Ethereum functionality. It makes managing state and blockchain interactions more intuitive.
-Viem is a TypeScript-first library built for working with Ethereum and other blockchain networks. It focuses on performance, developer experience, and extensibility, making it a powerful tool for interacting with smart contracts and building Web3 apps.
- Why Use It: Viem enhances development speed by providing efficient utilities and a modern approach to handling blockchain interactions. It pairs well with Wagmi and other Web3 libraries.